Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver, most commonly caused by viral infections (like hepatitis A, B, or C), though it can also result from alcohol, fatty liver, certain medications, or autoimmune diseases. It may be short-term (acute) or long-lasting (chronic), and it can affect how well the liver works over time.
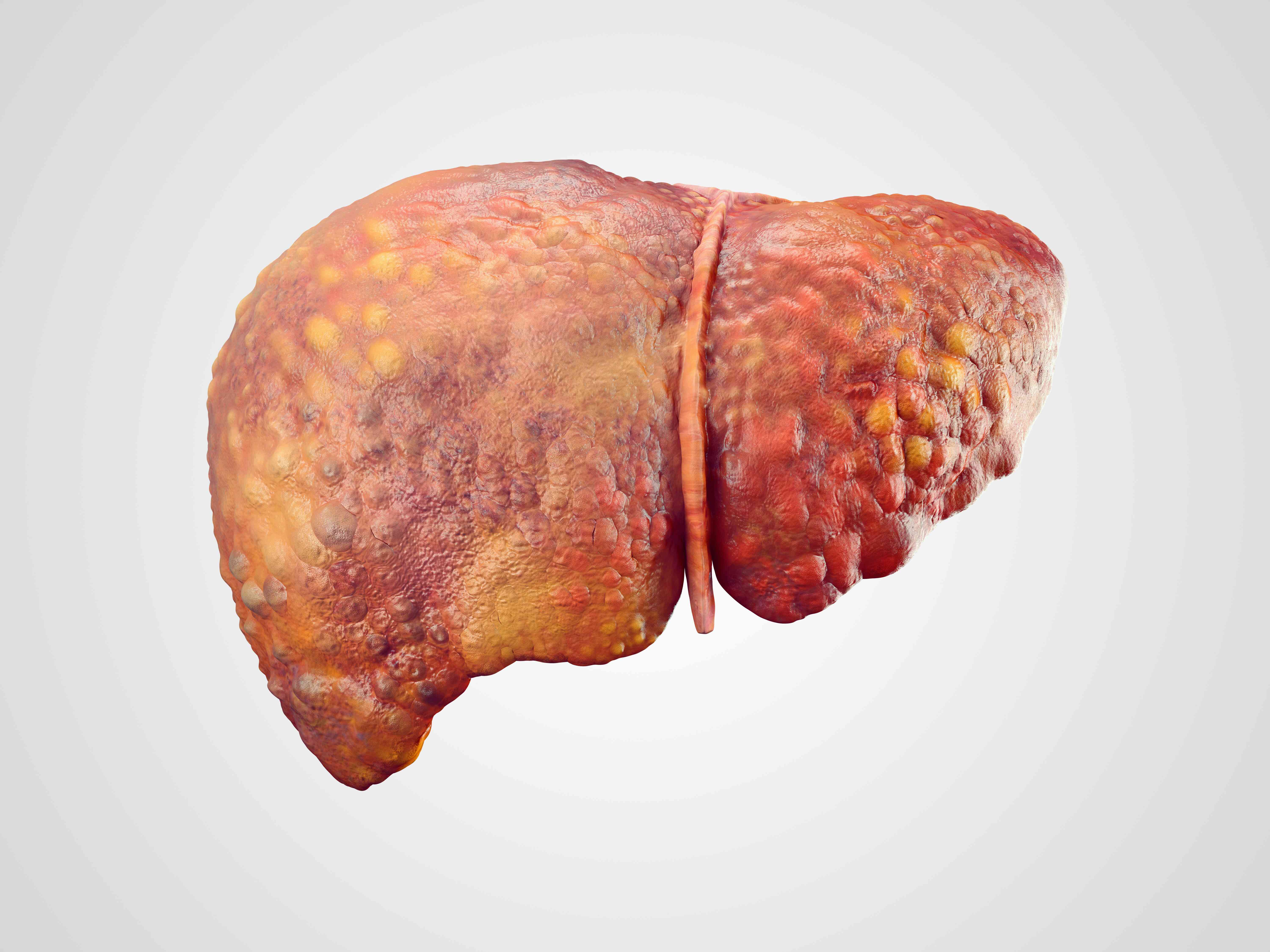
Liver cirrhosis is the result of long-term liver damage, where healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue (fibrosis). This scarring blocks blood flow and affects the liver function. Cirrhosis is the advanced stage of many liver diseases, including hepatitis and fatty liver disease.